The automotive industry has been growing in the past few years. New trends have made their way and new markets have opened up, thanks to disruptive innovation. Considering the past paced environment and innovations that take place daily, business models and industries are subjected to rapid growth, disruption and change.
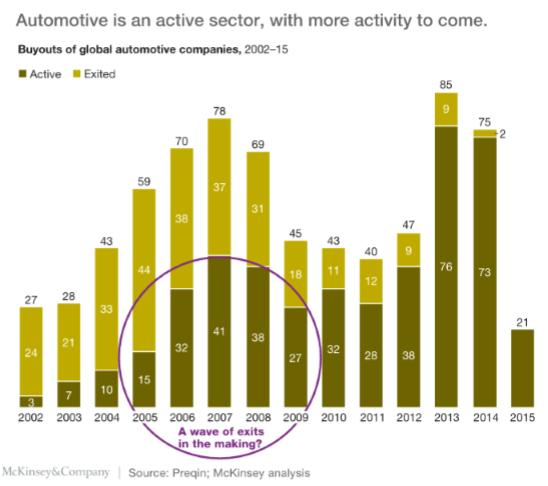
In the past decade, Automotive Industry has come up to be an active sector and forecasts show much more may come. It was suggested by Leslie S. Hiraoka (Prof. of Management Sciences at Kean University in Union, NJ and Associate Editor of Engineering Management Journal) in her book Global Alliances in the Motor Vehicle Industry that the globalization of the automotive industry has greatly accelerated during the last half of the 1990’s due to the construction of important overseas facilities and establishment of mergers between giant multinational automakers.
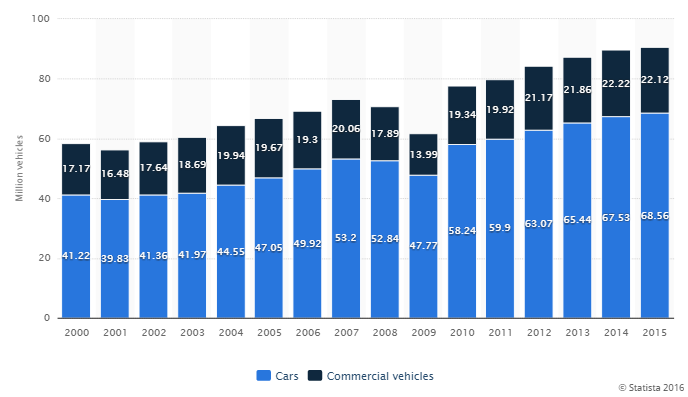
About 72.35 million cars were sold worldwide in 2015, and around 68.56 million cars were produced worldwide in the same year. Global car sales are expected to exceed 100 million units by 2020. United States became a key automotive market when Ford introduced assembly line car production in the early 1900s to mass-manufacture its Model T. Today, the Ford Motor Company still ranks among the leading manufacturers of passenger cars.
Few of the key trends that can be seen are:
- Changes In Customer Demand
Many customers are inclining towards greener, fuel efficient and sustainable vehicles. With the introduction of e-vehicles & alternative fuel such as Shale gas, CNG and others, gone are the days when the design and style was the major decision making factor. After the Volkswagen emissions scam, customers are more cautious and are hard to acquire.
- Changes in Brand Loyalty
Even the brand loyal customers are now rethinking their buying decisions as a result of surplus choices in the market. Impressing the customer remains harder than ever.
- Changes in Mobility
Mobility no longer means auto-mobility by default; the only thing that counts is efficient and inexpensive transport. Driverless cars are not the only trend challenging the automotive industry. Views about mobility, about what we can do with a car, about the status of owning a car, are in transition. The number of female buyers is increasing and becoming more and more commonplace.
- Technological Advances
The global automotive industry has witnessed a lot of transformation in the last two decades with the digitization of vehicles. Linking mobile devices to the vehicle creates many options. One can easily check how much fuel is left, the condition of the brakes, when maintenance is needed, etc. It can also be used as a car key, or for applying personal settings in a car you rent. Cars just might be the next big platform for application developers. McKinsey predicts up to 15% of new cars sold in 2020 could be fully autonomous.
The concept of ‘connected vehicles’, which focusses on connecting vehicles with the outside world and enhancing on-board experience, combines telecommunication and informatics to provide various services such as live traffic updates, smart routing and tracking, roadside assistance in case of accidents, automatic toll transactions, automatic parking / parking management, on-board entertainment, and much more.
- Resource Scarcity
According to recent growth figures, electric vehicles sales grew by 60% from last year. This is roughly equivalent to the growth forecasted by Tesla Motors, where production is expected to increase from 50,000 in 2015 to 500,000 in 2020. Assuming Tesla can meet their forecasts, and their current electric vehicle market share remains the same at 10%, if each electric vehicle roughly displaces 15 barrels of oil a year, the next oil crash could occur as early as 2023.
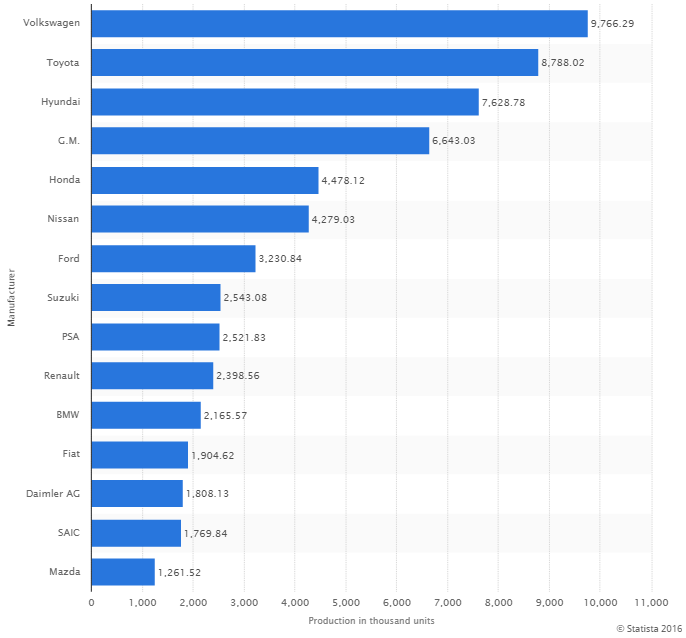
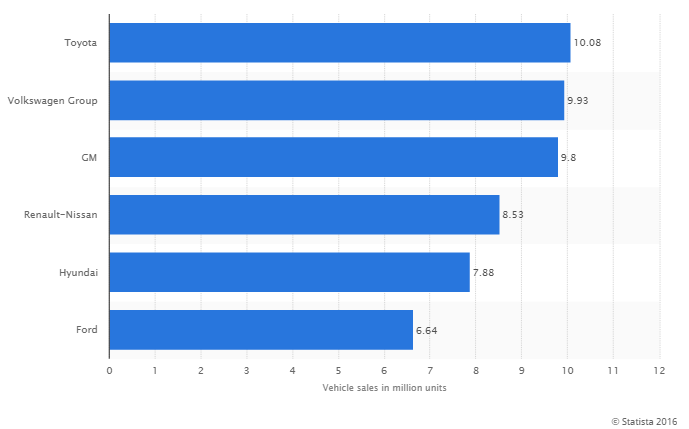
Related: The next revolution in the auto industry
Forecasts for Global Automotive industry for 2016:
- Sales
German supplier Continental forecasts global production of cars and light trucks to grow only slightly in 2016, to 89 million vehicles from about 88 million in 2015.
“For 2016, we see only very moderate growth in the auto industry,” Continental CEO Elmar Degenhart said at the Detroit auto show this week. China “is good for 3-4 points of growth in terms of production,” although that’s a slower rate than the country has seen in recent years. The CEO added he sees the U.S. vehicle market as “stable, with a slight positive upside.”
- Global Rental Industry
The global car rental industry is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2016 to 2021. The major drivers of growth for this market are rising global tourism industry, increasing globalization of corporate operations, and increasing income levels across the globe.
- Fuel Efficiency
Regulatory bodies are placing a strong focus on fuel efficiency for new vehicles. The Federal Government has set specific targets in the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards. The stated goal is to achieve fuel savings of 1.8 billion gallons (6.8 billion L) of fuel per year.
- Automated Cars
According to Continental’s road map for the technology by 2020, highly automated vehicles – those in which the drive doesn’t have to monitor the system but must be able to take control if warned by the car – should be on the road. Continental expects fully automated vehicles – in which the driver does not have to monitor the road or be prepared to take control – to be available for sales by 2025.

